Everyone experiences stress in one fashion or another. Stress is a very normal part of everyday life, and in some respects, it is necessary for our survival. However, any life event that pushes you to experience worry, fear, or uncertainty for prolonged periods can have negative impacts on your mental and physical health. For your well-being, it is vital to understand what stress is, and what types of stress exist. It is also important to know the causes of stress and the negative effects of stress on the mind and body so that you can deal with life’s stressors in a healthy way when they inevitably happen.
What Is Stress?
Psychological stress is defined as “a cognitive perception of uncontrollability and/or unpredictability that is expressed in a physiological and behavioral response.” [1]Koolhaas, J. M. Bartolomucci, A., Buwalda, B., de Boer, S. F. Flügge, G., Korte, S. M.Fuchs, E. (2011). Stress revisited: a critical evaluation of the stress concept. Neuroscience & … Continue reading In other words, stress is an experience of negative emotion (overwhelm, fear, pain, anxiety, anger, etc.) that can cause physical distress, elicit emotional distress, or bring about uncharacteristic behavior.
Types of stress include:
- Acute stress
- Episodic acute stress
- Chronic stress
Acute Stress
Acute stress typically occurs as a result of an unexpected life crisis, such as the death of a loved one, a serious car accident, or other traumatic experiences. This type of stress is termed ‘acute’ because the stress response in the body develops quickly, but the symptoms associated with the stressful event don’t usually last for a long period. Events that trigger acute stress are often severe in nature and the body’s stress response to the event can be mental, physical, or both.
Episodic Acute Stress
Episodic acute stress occurs when a person experiences frequent episodes of acute stress. These people may appear to always be flustered, in a hurry, easily irritated, or disorganized. People who suffer from episodic acute stress are usually taking on more responsibility than they can reasonably handle. As a result, they are unable to consistently tend to their physical, mental, and emotional health, and their well-being and personal relationships are negatively impacted.
Chronic Stress
When a person experiences prolonged periods of stress or overwhelm, they are in a state of chronic stress. Chronic stress occurs when a person experiences long-lasting, highly stressful events at a frequency that prevents their body’s relaxation hormones from adequately taking effect on a regular basis. As a result, their body constantly remains in a state of heightened physiological stimulation, impacting nearly every system within the body.
How Does Stress Affect the Mind?
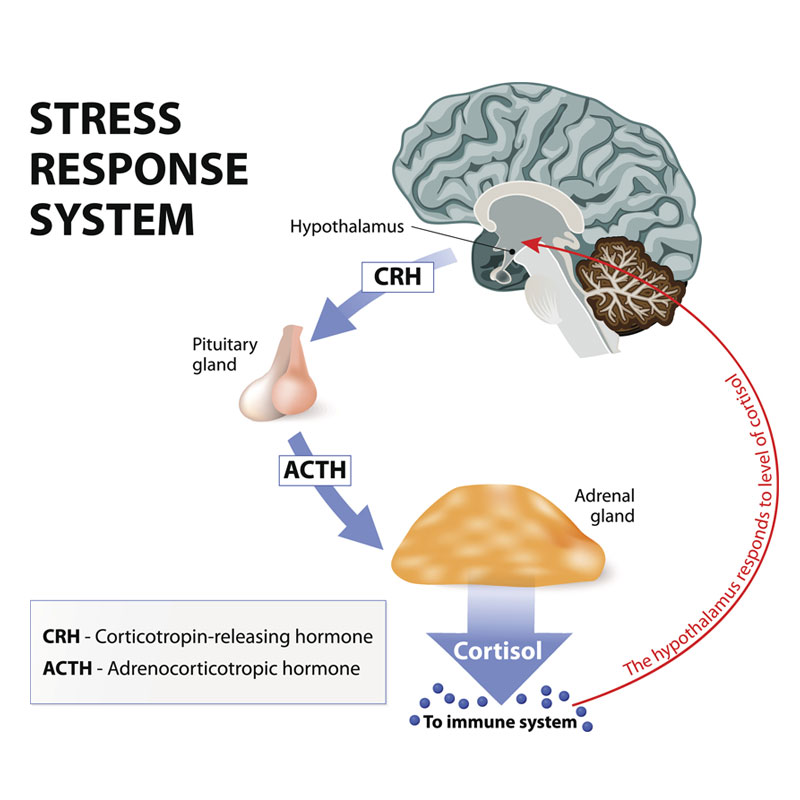
All forms of stress have effects on the brain. [2]Marin, M. F., Lord, C., Andrews, J., Juster, R. P., Sindi, S., Arsenault-Lapierre, G.,Lupien, S. J. (2011). Chronic stress, cognitive functioning, and mental health. Neurobiology of Learning and … Continue reading Acute sources of stress usually have temporary effects, and chronic stressors have effects that are longer lasting and more severe. Stress causes the body to release the stress-response hormone, cortisol, to help restore balance to the body after stressful events. This response is normal, and when our bodies get cortisol in moderation no real problems occur. However, when chronic stress is present, bodily systems make more cortisol than they can reasonably handle, which is highly problematic. [3]Dedovic, K., Duchesne, A., Andrews, J., Engert, V., & Pruessner, J. C. (2009). The brain and the stress axis: the neural correlates of cortisol regulation in response to stress. Neuroimage, … Continue reading
Long bouts of stress keep us in a state of stimulation that wears on the brain and its functions, eventually causing physiological and psychological issues, such as:
- Destroyed brain cells
- Disrupted synapse function
- Shrunken prefrontal cortex and enlarged amygdala (both are responsible for behavior regulation)
- Depression and/or anxiety
- Anger, restlessness, or irritability
- Feeling overwhelmed or unfocused
- Lack of motivation
- Insomnia or excessive sleeping
- Constant worry
- Memory or concentration problems
- Harmful decision making
Mental stress can greatly affect how you think and how you feel. Chronic mental stress can become so overwhelming that it dampens your ability to get through a normal day of responsibilities and make sound decisions. Some people cope with feelings of chronic stress through drug and alcohol use which can lead to addiction or even death. The negative impact of stress on mental health is a truly serious matter.
How Does Stress Affect You Physically?
The hormones the body produces are sent as signals to inform our body to function healthily. When stress is present, the signals are sent periodically or erratically, eventually leading to poor physical health. The hypothalamus works like a control center inside the brain, sending cortisol whenever you are in a situation that elicits a stress response.
Physical symptoms of stress include:
- Difficulty breathing
- Panic attacks
- Blurred eyesight or sore eyes
- Sleep problems
- Fatigue
- Muscle aches
- Headaches
- Chest pains
- High blood pressure
- Indigestion or heartburn
- Constipation or diarrhea
- Feeling sick, experiencing dizziness, or fainting
- Sudden weight gain or weight loss
- Developing rashes or itchy skin
- Sweating
- Menstrual cycle changes
- Worsening of existing physical health conditions
Adrenal Stress Test Kits
Fortunately, there are convenient ways for you to gain vital information about your mental and physical health from home. If you are interested in learning more about the effects of stress on your adrenal system, an Adrenal Stress Test Kit can give you results 5-7 days after you receive the test. Measuring the health of your adrenal system with a stress kit will provide you with insight into the functioning of your metabolism, immune system, and blood pressure, as well as your body’s response to stress.
Sleep Balance Test Kits
Similarly, a Sleep Balance Test Kit helps assess how the stressors in your life are impacting your ability to get a quality night’s rest. In just 5-7 days of receiving your kit, you will gain a clear idea of how your body’s response to stress is affecting your sleeping patterns.
Neurotransmitters Test Kits
Finally, a Neurotransmitters Test Kit provides an assessment of your psychological health and will help get to the root of conditions such as mood disorders, adrenal dysfunction, lack of ambition, libido dysfunction, Obsessive-Compulsive Disorder (OCD), and Attention-Deficit/Hyperactivity Disorder (ADD/ADHD).
Recognizing Stress Triggers
You can’t get through life completely stress-free, but you can better equip yourself to handle stressful events as they occur, which is practicing stress management. [5]Stojanovich, L. Marisavljevich, D. (2008). Stress as a trigger of autoimmune disease. Autoimmunity Reviews, 7(3), 209-213.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2007.11.007 One of the best ways to accomplish this is to become familiar with what types of situations or events “trigger” you, causing you to feel stressed. Recognizing your stress triggers and engaging in stress management will allow you to come up with coping strategies to work through stressful situations.
Methods for Learning to Relax
Relaxation is a vital component of managing everyday stress. You can employ several techniques to find more peace and mental calm throughout long and stressful days. It may be helpful to start with activities you already enjoy and add on new practices as you determine which relaxation methods help you cope with stress the most effectively. The benefit of having relaxation techniques in your stress management arsenal can prove to be invaluable to the progress of your mental and physical health. [6]Norelli, S. K. Long, A.Krepps, J. M. (2020). Relaxation techniques.In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513238/ Life is full of challenges and responsibilities, but they don’t have to be unnecessarily overwhelming.
Visualization
Through visualization, you can increase mind-body awareness and reduce stress by visualizing peaceful imagery, calmly repeating positive mantras, and using those peaceful cues to slow your breathing and tap into your physical state.
Progressive Muscle Relaxation
Progressive muscle relaxation involves a mind-body connection by making you more aware of your physical state through the tensing and relaxing of different areas of your body. You want to focus on tensing and subsequently relaxing one group of muscles at a time. Working from head to toe – or starting at your toes and working upward – are both good ways to practice. Repeat the process of tensing your muscles for 5 seconds and relaxing them for 30 seconds.
Both relaxation techniques are excellent practices to bring you into awareness of how your body processes stress. It is encouraged to try both techniques to see which one is most beneficial.
Benefits of Relaxation Techniques
Some of the benefits of these techniques are:
- Lowered blood pressure
- Improved digestion
- Improved blood sugar levels
- Reduction of stress hormones
- Increased blood flow to major muscles
- Reduction of muscle tension and chronic pain
- Improved focus
- Improved mood
- Improved sleep quality
- Boosted confidence
- Better problem solving and decision-making
Remember that both relaxation techniques involve channeling your attention toward something that is calming. You will need to practice these techniques over time by slowing down and being intentional to increase mind-body awareness.
It’s Important to Identify Stress and Relax
Once you have identified your stress triggers, you can practice stress management by lessening stressors or avoiding them completely. Furthermore, the development of stress management strategies can help you cope when you cannot avoid a stressful experience. Proactive stress management is the best way to restore your mind and body through stressful events and will help you maintain resiliency. A healthier life begins with understanding how stress impacts you, and how you can successfully combat it with stress management.
Chief Operating Officer, The Compounding Pharmacy of America
Matthew Poteet, Pharm.D. graduated with Honors from Lee University with a Bachelors of Science in Biological Science. After his undergraduate training, he completed the Doctor of Pharmacy program at Mercer University Southern School of Pharmacy, graduating in 2004. Dr. Poteet has spent much of his pharmacy career on staff at two of the most prestigious academic teaching hospitals in the Southeast; Emory University in Atlanta and Vanderbilt University Medical Center in Nashville. At these institutions he received extensive experience and training in sterile products compounding.
He returned home to East Tennessee in 2010, where he has held the position of Pharmacy Director at two sterile products pharmacies in Knoxville. Matthew lives in Knoxville with his wife, Chris. Dr. Poteet is Tennessee’s first Board Certified Anti-Aging Pharmacist by the American Academy of Anti-Aging Medicine.
Sources:
| ↑1 | Koolhaas, J. M. Bartolomucci, A., Buwalda, B., de Boer, S. F. Flügge, G., Korte, S. M.Fuchs, E. (2011). Stress revisited: a critical evaluation of the stress concept. Neuroscience & Biobehavioral Reviews, 35 (5), 1291-1301. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neubiorev.2011.02.003 |
|---|---|
| ↑2 | Marin, M. F., Lord, C., Andrews, J., Juster, R. P., Sindi, S., Arsenault-Lapierre, G.,Lupien, S. J. (2011). Chronic stress, cognitive functioning, and mental health. Neurobiology of Learning and Memory, 96 (4) 583-595. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.nlm.2011.02.016 |
| ↑3 | Dedovic, K., Duchesne, A., Andrews, J., Engert, V., & Pruessner, J. C. (2009). The brain and the stress axis: the neural correlates of cortisol regulation in response to stress. Neuroimage, 47(3), 864-871. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.neuroimage.2009.05.074 |
| ↑4 | McEwen, B. S. (2008). Central effects of stress hormones in health and disease: Understanding the protective and damaging effects of stress and stress mediators.European Journal of Pharmacology, 583(2-3), 174-185.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ejphar.2007.11.071 |
| ↑5 | Stojanovich, L. Marisavljevich, D. (2008). Stress as a trigger of autoimmune disease. Autoimmunity Reviews, 7(3), 209-213.https://doi.org/10.1016/j.autrev.2007.11.007 |
| ↑6 | Norelli, S. K. Long, A.Krepps, J. M. (2020). Relaxation techniques.In StatPearls [Internet]. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK513238/ |






 Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Subscribe to Our Newsletter


