Psoriasis is a chronic condition that affects more than 8 million people in the United States (National Psoriasis Foundation, 2023). While it can appear at any age, it is most commonly diagnosed between the ages of 15 and 35. The condition presents in cycles, often flaring and subsiding over time, and can significantly impact quality of life due to physical discomfort, visibility of lesions, and associated comorbidities such as arthritis or depression.
First-line therapies often involve topical corticosteroids, coal tar, or vitamin D analogues. However, some patients may not respond well to these therapies, while others may experience side effects with prolonged use. In such cases, personalized treatment, including compounded medications tailored to the patient’s specific needs, may provide a more targeted approach to care.
What Is Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is a chronic autoimmune condition that researchers in the International Journal of Molecular Science (Tashir & Sawada, 2022) associated with systemic inflammation. This inflammation causes the body’s immune system to mistakenly accelerate the life cycle of skin cells.
Typically, skin cells grow and shed over a cycle of roughly 28–30 days. In individuals with psoriasis, this process accelerates dramatically, sometimes occurring in just 3–7 days, resulting in the accumulation of immature skin cells on the surface. The result is the development of thickened, scaly plaques that can appear anywhere on the body.
Common triggers for psoriasis flare-ups include:
- Stress
- Illness
- Cold, dry weather
- Certain medications
- Skin injuries
There are several clinical subtypes of psoriasis, each with distinct features:
- Plaque Psoriasis – The most common form of psoriasis, plaque psoriasis appears as raised, red patches covered in silvery-white buildup, often on the elbows, knees, scalp, or lower back.
- Guttate Psoriasis – This type of psoriasis is characterized by small, dot-like lesions and is frequently triggered by infections like strep throat.
- Inverse Psoriasis – Inverse psoriasis presents as smooth, shiny lesions in body folds (e.g., the underarms or groin).
- Pustular Psoriasis – This type of psoriasis features white pustules surrounded by red skin and is often localized to the hands and feet/
Common symptoms of psoriasis include:
- Persistent itching, burning, or stinging
- Cracked skin that may bleed
- Thickened or ridged nails
- Emotional distress due to visibility or discomfort
The chronic nature of psoriasis and its potential physical and emotional burden make it a condition that often requires long-term, adaptive management strategies. Many individuals live with cycles of flares and remissions, with symptoms influenced by genetics, immune function, and environmental triggers.
Standard Treatment Approaches
Managing psoriasis typically involves a tiered approach based on the severity of symptoms, affected body surface area, and response to previous therapies. While many individuals experience some relief with standard treatment options, it is common for patients to cycle through multiple medications over time, especially as the condition evolves or flares.
As such, there are many accepted treatments for psoriasis, including:
Topical Treatments
Topical corticosteroids are the primary option for those experiencing mild or moderate psoriasis. According to a 2025 StatPearls report (Gabros et al., 2025), topicals can help reduce inflammation, itching, and plaque formation. However, this can also lead to skin thinning, tachyphylaxis, and reduced efficacy over time if utilized in the long term.
Some other common topical treatments include:
- Vitamin D Analogues, including calcipotriene, which, when used along with corticosteroids, can slow the growth of skin cells.
- Coal tar, which is a more traditional method that helps reduce certain side effects, such as itching and inflammation.
- Salicylic acid, which is often used to soften and remove scales.
These options can help alleviate symptoms, but they are not one-size-fits-all. In some cases, more extensive treatment is necessary. Additionally, some patients may require multiple treatments.
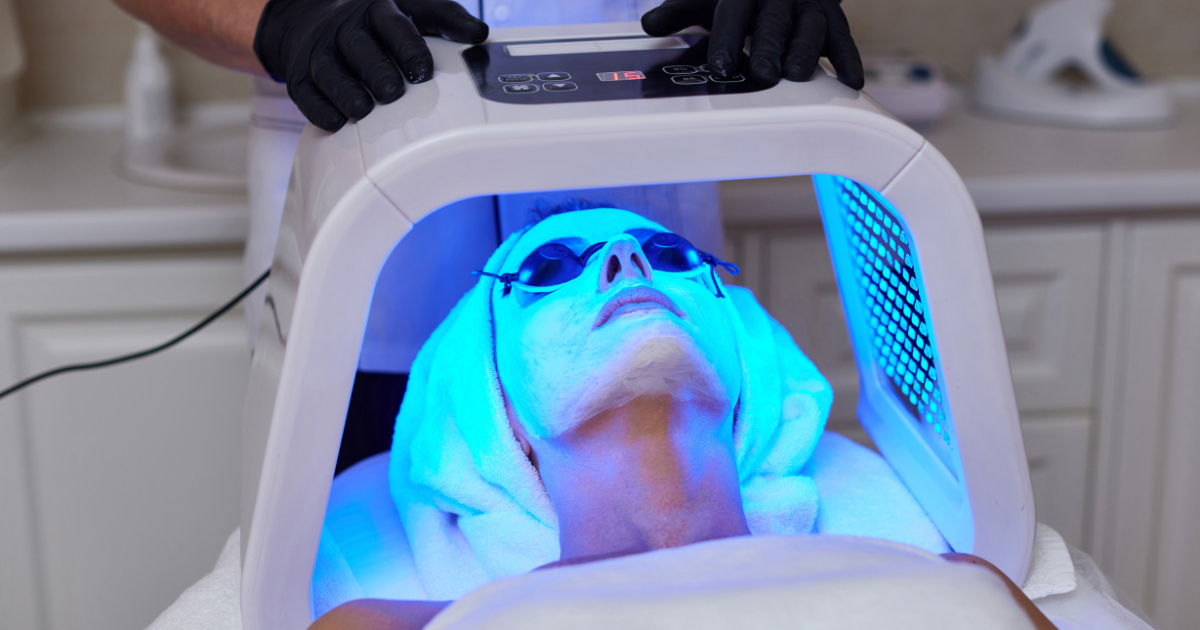
Phototherapy
Phototherapy is also known as light therapy, typically using UV light to treat various skin conditions, including psoriasis. It can help reduce inflammation and slow down skin growth. However, it may not be suitable for everyone, and those who undergo phototherapy will usually require multiple rounds of treatment.
Systemic and Biological Therapies
In some extreme cases of psoriasis, systemic immunosuppressants and biologic agents can be used. While these can provide intense improvement, they also present a risk of infection. Both types of treatments should be used sparingly and necessitate careful monitoring.
Due to the various types of treatments available for the different types of psoriasis, therapies should be tailored to the individual patient and their needs. Some treatment options may be appropriate for one person and not another, depending on the circumstances. Often, a custom blend of treatments is necessary to address psoriasis symptoms.

How Compounding Pharmacies Support Psoriasis Management
Psoriasis can be difficult to manage. For some patients, standard treatment plans are sufficient, while many others may notice their symptoms remain unchanged or worsen. Both groups may experience additional symptoms, whether caused by the condition or its treatments, that make life uncomfortable. Fortunately, compounding pharmacies can provide additional support.
Compounding pharmacies enable pharmacists to create a customized medication plan to address psoriasis symptoms, side effects, and unique patient needs. This plan can consider factors like patient skin type, lifestyle, sensitivities, allergies, and more. Together, a compounding pharmacy and a physician can find the ideal solution for a complex issue.
Compounding pharmacies can:
Customize Medication Strength and Adjunctive Therapy Combinations
Topical corticosteroids are often the first treatment prescribed to psoriasis patients. However, not everyone responds well to the standard prescription. For example, if a patient has a plaque in a highly sensitive area, they may need ultra-low-potency steroids instead. Sensitive patients who have more stubborn plaques may need a medium-strength option. To help patients who do not respond well to the standard formulation, compounding pharmacies can adjust the potency of the medication as well as secondary ingredients that address absorption rate and hydration.
In this way, compounding allows for flexibility in a patient’s treatment plan. Compounding pharmacists can prepare one product that contains additional moisturizing agents as well as a customized dose of corticosteroids to enable moisturization without interfering with absorption.
Customize Medication Forms and Adjust Inactive Ingredients
Another benefit of compounding is the ability to adjust the medication form. While topical creams are most common, some patients find them too oily. Others find creams difficult to apply to hard-to-reach trouble spots, including the scalp. Still others are allergic to the inactive ingredients found in common topical creams.
Compounding pharmacists can create a variety of topical forms, such as creams, oils, gels, foams, and sprays, to reduce unpleasant side effects and improve absorption in troublesome areas. There are also hypoallergenic options for those who need them. These options allow for greater comfort and consistency.
Customize Add-On Ingredients
In some instances, compounding pharmacists can create unique formulations that feature additional ingredients necessary to soften plaques or reduce inflammation. These can include:
- Salicylic acid, which helps remove scales
- Urea, which hydrates and breaks down thickened skin
- Coal tar or botanical agents, for patients who want to limit steroid use
The patient’s treatment history, unique needs, and other various aspects of their psoriasis condition will influence which add-ons are most appropriate for their treatment plan.
Engage in a Collaborative Process
It’s worth noting that the ideal compounded psoriasis medications can only be created in collaboration with a knowledgeable prescriber. Compounded medication is a component of a treatment plan created for a unique patient. Every component should be carefully selected with the needs of the patient, their particular case of psoriasis, and their medical history in mind.
Compounding is not necessary for every person with psoriasis, but it is a viable option, particularly for those who have not achieved the desired results from standard treatment plans.
Benefits of Compounded Psoriasis Medications
Psoriasis treatment is not a one-size-fits-all solution; not every patient responds well to standard treatment options. This is where compounded medications come in. Compounding pharmacies can consider the patient’s individual condition, needs, and circumstances, like lifestyle and tolerance levels, while creating customized medications.
Compounded psoriasis medications can offer many benefits.
Improved Treatment Adherence
Because compounded medications are tailored to a patient’s individual needs, patients typically adhere more closely to treatment instructions. Compounded medications can feature a better-textured formula, more tolerable ingredients, and/or a simplified application process. Such customizations can increase the likelihood of a patient continuing treatment and achieving a positive outcome.
Synergy in Medications
Combining several active components into a single formula is another advantage of compounding. For instance, a keratolytic ingredient like salicylic acid can be used in conjunction with a corticosteroid to help dissolve plaques and reduce inflammation. This strategy can increase treatment effectiveness and simplify treatment by reducing the number of products required.
Fewer Irritants and Allergens
Compounded medications can replace irritants with hypoallergenic options for sensitive patients. Standard medications may include fragrances or preservatives that can irritate the skin and increase the risk of flare-ups. This can be especially triggering for patients with facial or intertriginous psoriasis, where the skin is thinner and more reactive. A compounded medication with alternative ingredients can reduce flare-ups while treating psoriasis.
Flexible Dosing
Flexible dosing in compounded medications can enable providers to adjust the amount of the active ingredient in one application of the product. This can be especially useful for young children and elderly patients. Patients with medication sensitivities, those who require medication to treat psoriasis in a sensitive area, and patients with mild or aggressive forms of psoriasis can also benefit from flexible dosing.
Compounding provides more opportunities for patients to treat their psoriasis by offering a personalized approach. With properly tailored compounded medications, some patients may experience better symptom management and improved quality of life.

Safety Considerations
Compounded medications are a tailored approach to managing psoriasis, but that does not mean they are without risks and side effects. Those who receive compounded medications should still exercise proper safety measures when implementing psoriasis treatments, especially those involving corticosteroids. StatPearls research published in 2023 (Yasir et al., 2023) cautions that improper or long-term use of corticosteroids can sometimes cause adverse side effects, including thinning of the skin, stretch marks, or a rebound worsening of symptoms when stopped abruptly.
Whether you’re taking standard psoriasis treatments or are considering a compounded version, these tips can help you ensure safety.
Monitor with a Provider
Due to the risks associated with psoriasis, it’s important to have your care closely monitored by your healthcare provider. Your provider is familiar with your situation, including the type and location of your psoriasis as well as your age, medical history, and how you respond to treatment. Following up with your provider can help you analyze your progress, adjust treatment, respond to any side effects, and minimize negative outcomes.
Obtain a Valid Prescription
All compounded medications require a valid prescription from your healthcare provider. Any changes and adjustments must also be initiated by your provider. A reputable compounding pharmacy will demand a current prescription before creating your customized product.
Compounded medications are not evaluated by the FDA for safety or efficacy in the same way as commercially manufactured drugs. However, they are regulated under Section 503A of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act and must be prepared by licensed pharmacists following strict USP <795> and USP <797> standards. Many pharmacies also seek accreditation through organizations like the Pharmacy Compounding Accreditation Board (PCAB) to ensure the highest quality and safety.
Follow All Instructions
It’s also important to follow the instructions and dosage recommendations that accompany your compounded medication. Your prescription is tailored to your specific clinical needs. This ensures that dosing, ingredients, and delivery methods are all medically appropriate. Using the medication as instructed ensures both safety and efficacy and gives you the best chance at addressing your symptoms.
Personalized Options for Psoriasis Care
When common psoriasis solutions are not appropriate, compounding pharmacies can provide personalized compounded medications that suit the patient, providing them with safer, more effective treatment, such as topical dermatology medications. Compounding solutions could help you improve the way you manage your psoriasis and alleviate troublesome symptoms.
Ask your provider if compounded formulations could help you manage your condition more effectively.
*Editor’s Note: This article was medically reviewed for accuracy and updated in June, 2025. Older articles on this topic have been updated and consolidated into this comprehensive guide.
Sources:
- National Psoriasis Foundation. (2023). Psoriasis statistics. https://www.psoriasis.org/psoriasis-statistics/
- Tashir, M., & Sawada, A. (2022). Psoriasis and systemic inflammation. International Journal of Molecular Sciences, 23(11), 6344. https://pmc.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/articles/PMC9028262/
- Gabros, S., Nessel, T. A., & Zito, P. M. (2023). Topical corticosteroids. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK532940/
- Yasir, M., Goyal, A., & Bansal, P. (2023). Corticosteroid adverse effects. In StatPearls. StatPearls Publishing. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK531462/
- U.S. Food and Drug Administration. (2023). Section 503A of the Federal Food, Drug, and Cosmetic Act. https://www.fda.gov/drugs/human-drug-compounding/section-503a-federal-food-drug-and-cosmetic-act
- United States Pharmacopeia. (2023). General chapter <795> pharmaceutical compounding – Nonsterile preparations. https://www.usp.org/compounding/general-chapter-795

Compounding Pharmacy of America is committed to delivering reliable, accurate, and actionable health information to empower you on your wellness journey. Our content is created and reviewed by a dedicated team of professionals, including experienced writers and licensed healthcare experts.
Learn More About Compounding Pharmacy of America Editorial Team





 Subscribe to Our Newsletter
Subscribe to Our Newsletter
